What foods to avoid with ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is a part of a gathering of illnesses called inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
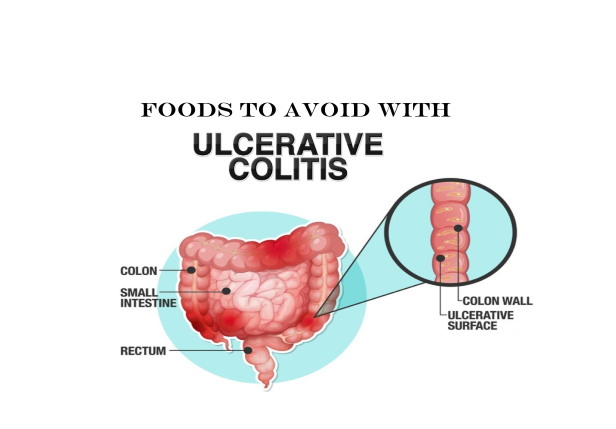
It is the point at which the covering of your digestive organ (the colon or enormous gut) and your rectum become red and enlarged (inflamed). The aggravation often starts in your rectum and lower digestive tract and climbs to the entire colon.
Ulcerative colitis doesn’t typically influence the small digestive tract. Yet, it can influence the lower segment of your small digestive system called the ileum.
The aggravation sources loose bowels, making your colon void itself recurrently as the cells on the layer of the colon bite the dust and fall off open injuries (ulcers) structure. These ulcers might cause discharge, bodily fluid, and bleeding.
Much of the time, ulcerative colitis begins between the ages of 15 and 30. Some of the time, youngsters and more aged individuals get it. It influences all kinds of people and appears to run in certain families (genetic).
Ulcerative colitis is a long-haul (constant) infection. Sometimes, your side effects disappear, and you go away for quite a long time or even years. Yet, the side effects will return.
If some stroke of good luck impacts your rectum, your risk of colon disease isn’t higher than ordinary. Your risk is higher than typical, assuming that the illness influences part of your colon, and most noteworthy, in the event that it influences your entire colon.
In uncommon cases, when extreme issues occur, ulcerative colitis can prompt passing away (death).
What causes ulcerative colitis?
Specialists don’t have the foggiest idea of what causes ulcerative colitis.
An infection or microorganisms may influence the body’s contamination-battling (invulnerable) framework. The resistant framework might cause strange redness and expansion (aggravation) in the gastrointestinal wall that doesn’t disappear.
Many individuals with ulcerative colitis have unusual invulnerable frameworks. However, specialists couldn’t say whether insusceptible issues cause the sickness. They additionally couldn’t say whether ulcerative colitis might create invulnerable issues.
No fix exists aside from a medical procedure to eliminate the colon.
Who is in danger of ulcerative colitis?
A few things might put you at higher risk for ulcerative colitis. These incorporate:
- Age. The sickness most frequently begins when you are between the ages of 15 and 30 years of age.
- Family ancestry. Having a relative or close family member with ulcerative colitis raises your risk of sickness.
- Race and nationality. It happens all the more frequently in white, endlessly individuals of Jewish descent.
What are the side effects of ulcerative colitis?
Every individual’s side effects might shift. The most well-known side effects include:
- Tummy pain
- Extremely bad looseness of the bowels
- Outrageous sleepiness (exhaustion)
- Weight reduction
- Loss of hunger
- Rectal bleeding
- Loss of body liquids and supplements
- Loss of blood (pallor) brought about by serious bleeding
Now and again, side effects may likewise include:
- Skin bruises
- Joint pain
- Redness and expanding (irritation) of the eyes
- Liver issues
- Feeble bones (osteoporosis)
- Rashes
- Kidney stones
The side effects of ulcerative colitis might seem to be other medical issues. Continuously see your medical services supplier certainly.
How is ulcerative colitis analyzed?
Your medical services supplier will give you an actual test. You will have some blood tests. The blood tests will look at the measures of your red and white platelets. On the off chance that your red platelet count is low, this indicates sickliness. If your white platelet count is high, this indicates redness and enlarging (irritation).
How is ulcerative colitis treated?
- Your medical services supplier will make a consideration plan for you given:
- Your age, generally speaking, health, and past health
- How serious your case is
- How well do you handle specific meds, medicines, or treatments
- Assuming your condition is supposed to deteriorate
- Your expected family plans, for example, getting pregnant
What you might want to do?
There is no unique eating regimen for ulcerative colitis. However, you might have the option to oversee gentle side effects by not eating food varieties that appear to disturb your digestion tracts.
Foods sources not to eat with ulcerative colitis
Are there normal food varieties to avoid assuming you have ulcerative colitis? OK, so we’ve stated that there are no reliable food varieties to keep away from that will decrease or dispense with ulcerative colitis side effects. Yet, there are food sources that you could attempt to stay away from during an eruption until your entrails quiet down. Those include:
1. High-fiber food varieties
Many individuals hail fiber as a supernatural supplement that can reduce your risk of creating coronary illness and type 2 diabetes and possibly offer some insurance against Crohn’s sickness flares — one more sort of IBD. What’s more, stacking up on fiber can help with those things.
Notwithstanding, certain individuals with ulcerative colitis might need to keep away from a high-fiber diet, contingent upon their side effects, as indicated by the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation. If looseness of the bowels is a sign of ulcerative colitis, you might need to eat less insoluble fiber since it moves food through the digestive system rapidly, exacerbating the issue.
To decrease your insoluble fiber admission, you might need to lay off beans (bye, stew) and different vegetables like chickpeas or lentils, cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower or kale, nuts, and entire wheat flour in your eating regimen to check whether your side effects improve.
Albeit high-fiber diets might influence certain individuals with ulcerative colitis during an eruption, specialists, by and large, prescribe trying to get sufficient fiber during reduction.
One 2017 survey of investigations discovered that it might assist with delaying periods without irritation — except in individuals who have injuries or a restricting of the intestine. “In those patients, we truly do exhort less fiber since filaments can bunch up and cause an impediment or constipation.”
2. Food sources containing FODMAPs
FODMAP embodies fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols. These short-chain starches are challenging for our bodies to process, can create gas, and increment liquid in your colon — eventually causing looseness of the bowels and gastrointestinal trouble in certain individuals. They’re available in many food sources, including onions, vegetables, frozen yogurt, apples, honey, and counterfeit sugars.
Specialists generally prescribe a low-FODMAP plan to treat the peevish gut condition (IBS), a term that depicts an assortment of side effects, including stomach torment, bulging, gas, and loose bowels or clogging.
Individuals with IBS don’t have irritation in the gastrointestinal system like those with IBD do. Notwithstanding, ulcerative colitis and IBS share some normal symptoms5, so your primary care physician might suggest attempting a low-FODMAP diet in the event that you have ulcerative colitis.
Specialists are concentrating on whether low-FODMAP diets can assuage ulcerative colitis eruptions, yet up until this point, studies have been little. A 2016 review study in the diary Inflammatory Bowel Diseases found that a low-FODMAP diet diminished side effects in 38 ulcerative colitis patients6.
More exploration concentrating on bigger quantities of individuals is important to decide if FODMAPs are a basic figure for ulcerative colitis side effects. In any case, narratively, certain individuals with ulcerative colitis report that controlling their FODMAP admission appears to help their stomach symptoms.
At first, the low-FODMAP diet is exceptionally prohibitive: The thought is to remove all FODMAPs before leisurely once again introducing some to figure out which you can endure. Along these lines, working with your health group while rolling out any dietary improvement to avoid wholesome lacks is vital.
3. Cheddar, milk, and dairy items
Dairy is tricky because lactose intolerance — or even an all-out dairy sensitivity — can sometimes be confused with an ulcerative colitis flare-up. “Something we propose is in the event that you’re feeling sick with things you’re eating, give a shot to cutback the dairy. On the off chance that that aide perhaps gets tried for lactose intolerance, which is a simple and justified test.”
Lactose intolerance and dairy sensitivity are totally different, even though some side effects are comparable, similar to stomach squeezing and loose bowels. With lactose intolerance, your body doesn’t deliver sufficient lactase, which is a chemical that permits you to process lactose, the fundamental sugar tracked down in dairy.
Lactose intolerance isn’t a crisis circumstance, regardless of whether it seems like a restroom crisis. If you have a dairy sensitivity, you are susceptible to explicit proteins tracked down in dairy items, and your safe framework gets a move on you to consume them.
This can prompt an extreme hypersensitive response, which can turn hazardous. Regardless of which you may be managing, you’ll need to preclude an aversion to dairy as a reason for your GI uneasiness.
4. Food varieties containing gluten
Ulcerative colitis isn’t equivalent to celiac illness, in which gluten sets off the resistant framework to go after the small digestive system. Nonetheless, 2020 exploration shows that individuals with ulcerative colitis are bound likewise to have celiac disease.
On the other hand, you could have gluten responsiveness, meaning you don’t have an insusceptible reaction to gluten; however, you find it causes side effects including swelling, stomach agony, loose bowels, and weakness, which can likewise be all side effects of ulcerative colitis.
A 2014 Inflammatory Bowel Diseases study studied 314 individuals with an IBD — incorporating 122 individuals with ulcerative colitis — and found that 56.5% revealed less bulging while on a sans-gluten diet. Likewise, 42.6% revealed less loose bowels, 41.5% announced less stomach pain, and 38.3% detailed that they had fewer and less serious flare-ups.
In any case, don’t begin throwing out your #1 oat right now. A high-FODMAP starch called fructan is in large numbers of similar food varieties as gluten. So removing gluten implies you’re also disposing of numerous FODMAP food varieties, which can be an over-the-top change to take on without anyone else.
Likewise, with these food varieties, it’s a question of experimentation, and working with an expert can assist you with sorting out what’s happening as securely as could really be expected. “We don’t suggest gluten aversion in essence, and there’s no proof that gluten demolishes IBD.”
“Assuming someone has side effects, we’ll go down the record and take a stab at keeping away from gluten, stay away from FODMAPs, and if in any case they appear to answer, we’ll go down that way.”
5. Wine, beer, and other cocktails
Perhaps you’ve proactively seen that liquor tends to invigorate your digestive organs, which can aggravate the looseness of the bowels, as per the Mayo Clinic.
Yet, don’t raise your clenched hand to the sky and revile the liquor divine beings; analysts accept the added substance sulfite (read: not put there by the divine beings), tracked down in brew, wine, and ale, may deteriorate side effects, as opposed to the actual liquor — which welcomes us to the keep going thing on this rundown. (Note that sulfite awareness is believed to be uncommon and isn’t yet surely known).
Conclusion
We may not come in contact with much self-care while looking forward to our extremely busy everyday lives, but one must remember that ignoring critical health concerns while dealing with day-to-day chores might bring old age faster than you reach the right age.
You indeed are what you eat, and more bad stuff means the worst insides of your body. That’s why one must always tend to read the labels and nutrition count of food items they are purchasing.
Ulcerative colitis may not come into your attention cycle as it’s a problem only noticed once you get admitted to the hospital for some serious health reasons. Still, you should know that while you eat, you worry about your insides, too, so you don’t have to book an Uber or fill up your car tank to have frequent visits to the nearest hospital.